Wisdom teeth and their pull-out
As they generally erupt in the ages of twenties, they are called with this name or as wisdom tooth.
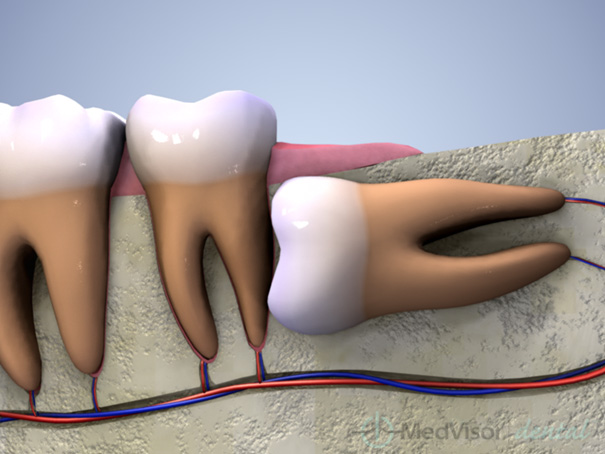
In which situations should wisdom teeth be pulled out?
- Decay: The saliva, bacteria and food wastes accumulate on the hole that the newly erupting tooth opens and they threaten both wisdom tooth and molar tooth. The heavy situations causing pain and infection and resulting with abscess can happen.
- Gingival disease (pericoronitis): On the gingival of the partially erupted wisdom tooth, an infection focus where the bacteria and food wastes are stored occurs. This situation causes oral malodor, pain, edema and trismus (situation of incomplete opening of the mouth). The infection can expand to cheek and neck via lymph.
- Pressure pain: During eruption, pressure can happen on the neighbor teeth due to space shortage and a pain can be felt due to compression. In some situations, this pressure causes edema and swelling.
- Reasons related to prosthesis: In a mouth for which prosthesis planning is made, it is required to take the wisdom teeth into account. Because, after the wisdom tooth is pulled out, it is required to make a new prosthesis according to the changing oral structure.
- Cyst formation: The cystic lesion cases that impacted tooth causes have been observed. The cystic lesions cause bone destruction, self-induced fractures on the jawbone and replacement or damaging of the surrounding teeth. To prevent the bone destruction, the tooth should be pulled out and cyst should be cleaned. If this cyst rarely expands to very wide areas, it can be transformed into tumors and cause self-induced fractures on the jawbone.
- Orthodontic reasons: If the erupting wisdom teeth will deform the arch form in case there is not any place on the completed dental arch, they are required to be pulled out.
It is an operation which is applied in the situations where the root canal treatment cannot be realized for removing the infections developing at the root edges of teeth and for cleaning of the inflamed root edge and the surrounding tissues to which the inflammation expands.




